A deep understanding of multipath characteristics is essential to design signal simulator and receiver in global navigation satellite system (GNSS) applications. As a new constellation is deployed and more applications occur in the urban environment, GNSS statistical multipath models need further study.
Multipath model
We present statistical distribution models of multipath time delay, multipath power attenuation, and multipath fading frequency for a static carrier in the urban canyon environment. The raw data of multipath characteristics were obtained by processing real GNSS signal to study the statistical distribution. In addition, the detailed statistical characteristics for different elevations and orbits satellites was studied, and the parameters of each distribution were quite different. The research results will give useful guidance for GNSS simulator designers.
We choose Lujiazui, Shanghai, which is one of the most populated skyscraper areas in China, as the target urban canyon environment to study.
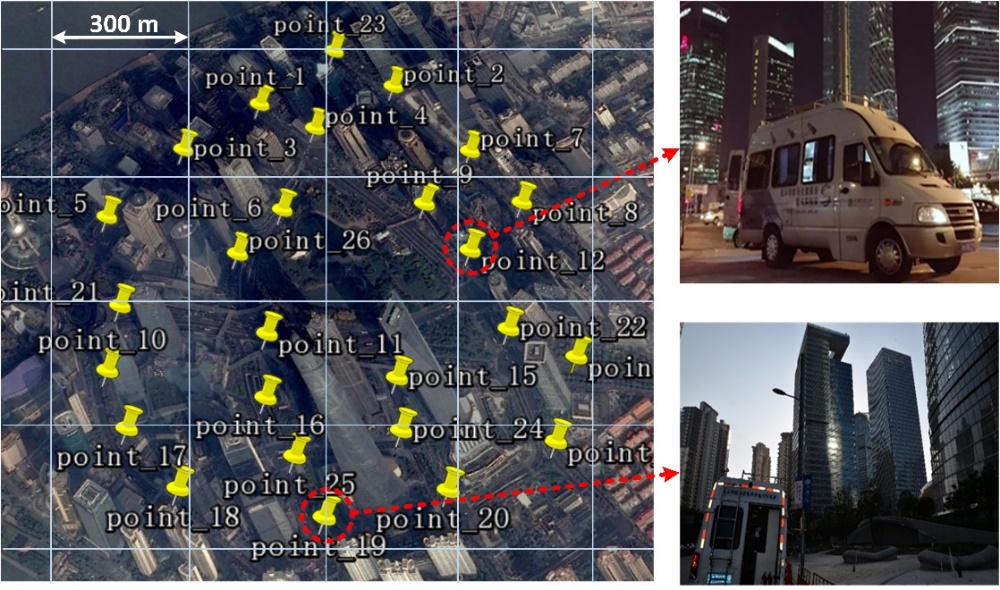
Satellite imagery of navigation signal collection spots
We built some statistical models of multipath characteristics by analysing the experimental data. The characteristics included multipath time delay, multipath power attenuation and multipath fading frequency. The raw multipath data of all collection spots were mixed in the following analysis to achieve reasonable statistical models.
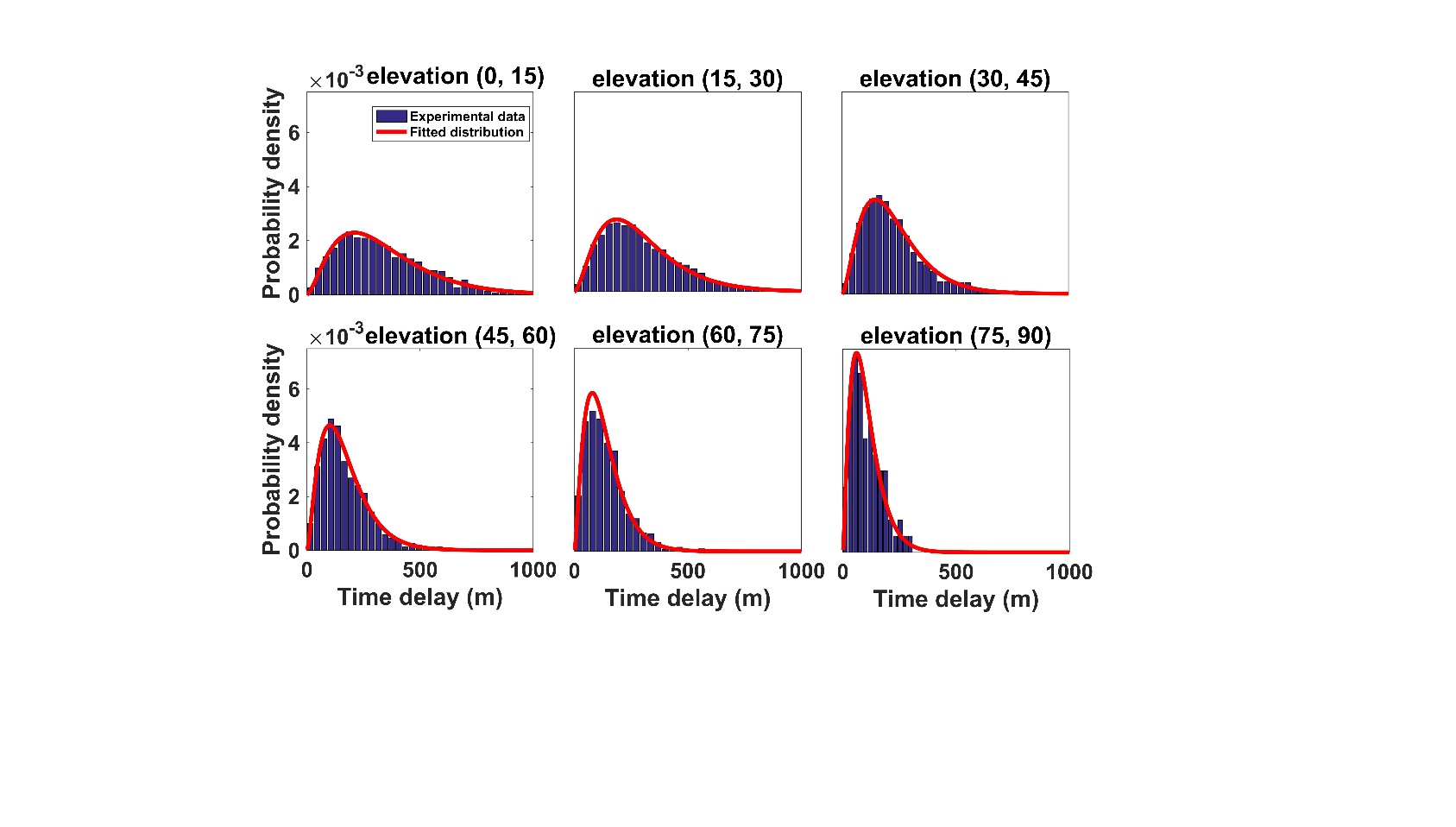
Distribution of multipath time delay in different elevation angle ranges
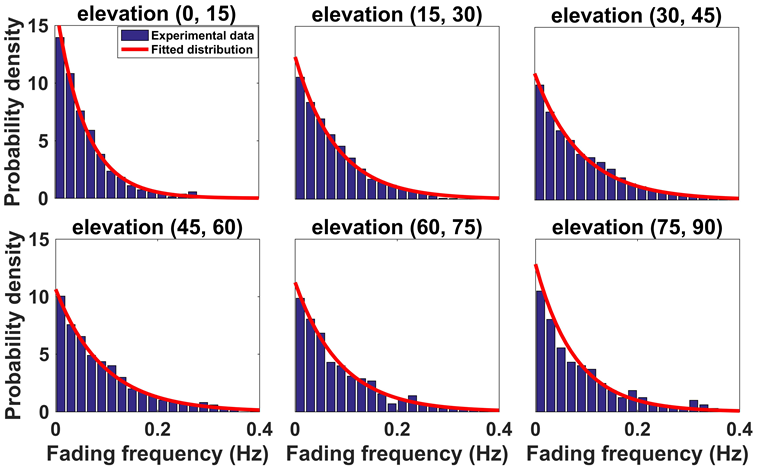
Probability distribution of multipath fading frequency for the MEO satellite
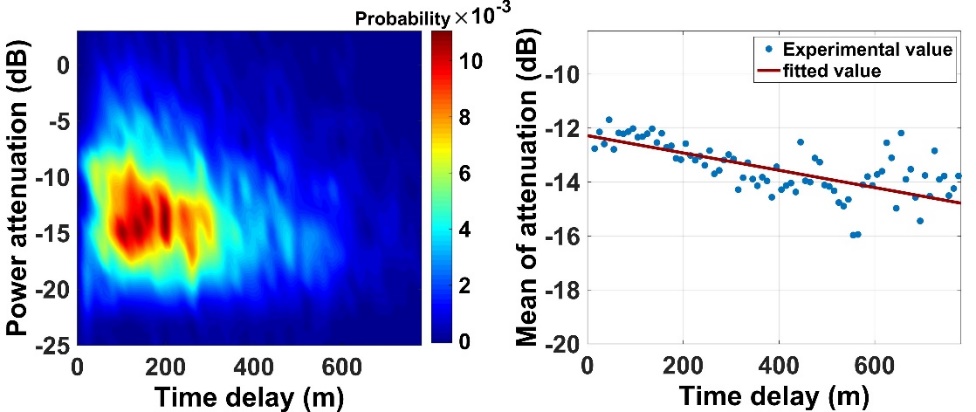
Probability of multipath power attenuation as a function of time delay
Several main conclusions can be drawn:
- The probability distribution of multipath time delay followed a gamma distribution, and the mean time delay was inversely proportional to the elevation angle.
- The mean multipath power attenuation linearly decreased as the multipath time delay increased, and the multipath attenuation was normally less than -17 dB.
- The probability distribution of the multipath fading frequency was axisymmetric around 0 Hz, and it followed a double-sided exponential distribution.
- For different elevations and different obits satellites, the type of distribution function to characterize each core parameters was the same, but the feature parameters were different.
Signal attenuation model
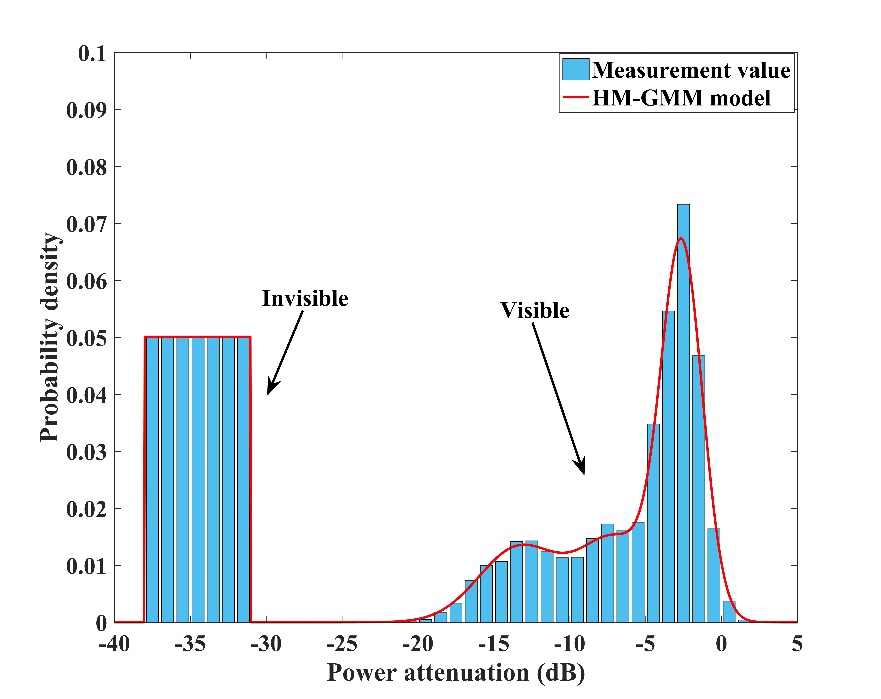
We research the characteristics of signal attenuation for both GPS and BDS GEO satellite in urban, suburb, viaduct-down and viaduct-up environment. Here, a hidden Markov Gaussian mixture model (HM-GMM) is proposed to describe the characteristics of signal power attenuation. The statistical model is composed of four states which contain one invisibility state and three visibility states. For each visibility state, the probability density of signal power attenuation follows Gaussian distribution. The invisibility state means that no signal can be detected by receiver. The expectation maximization (EM) algorithm is used to calculate all the parameters of HM-GMM including state transition matrix, probability matrix and parameters of each Gaussian distribution. In the experiment, the raw data of signal power attenuation is measured by a business receiver, and the receiving antenna is mounted on a van.
Four types of environment are selected to perform the experiment, and they are urban, suburb, viaduct-up (on the viaduct) and viaduct-down (under the viaduct) respectively. These environments are the most typical types in the city.
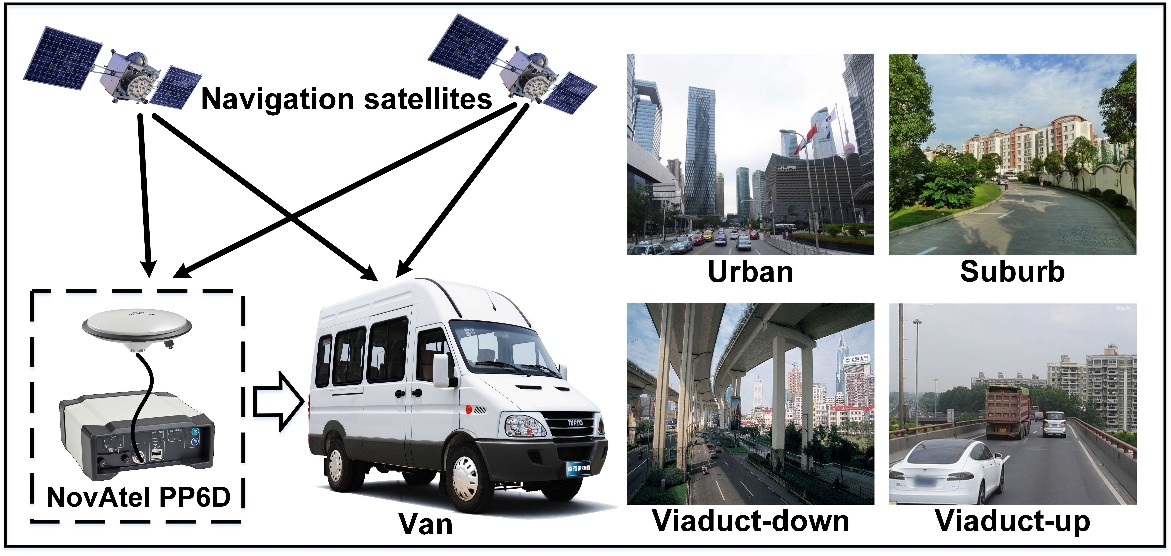
It can be seen that the environmental characteristics of different types are great different from Figure 2. A visualized description of each type is given as follows:
- Urban: In urban environment, there are many skyscrapers on both sides of the road. The GNSS signal will be easily blocked and multipath interference is serious.
- Suburb: The suburb environment is mainly composed of low-rise buildings and lush trees. The signal quality will be good when the satellite elevation is high.
- Viaduct-down: In viaduct-down environment, there is a large blocking area on the top of the antenna. The satellite signal will be received, when its elevation is near 45 degree.
- Viaduct-up: In viaduct-up environment, the signal quality is best among these four types, especially for the satellite with low elevation.
The HM-GMM model is built to describe the probability distribution of attenuation value. The following figure gives the probability histogram of measurements and the fitted model. It must be noted that only the measurements of visibility state is valid, and the measurements of invisibility state is just an illustration to describe the invisibility probability. Three order Gaussian mixture distribution is used to fit the visibility measurements, which can achieve a good fitting accuracy.